If you, or a member of your family has been diagnosed with Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), you may have questions about the disease and its treatment, especially if your doctor has recommended Angioplasty and implantation of a Stent. This booklet is written in a friendly ‘Question & Answer’ format to provide you with basic information on Angioplasty and to allow you to prepare for the procedure. If you have any additional questions after reading this booklet, please discuss with your Doctor
WHAT IS CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE?
The heart is a powerful muscular organ requiring adequate supply of oxygen to function efficiently. Oxygen-rich blood is carried to the heart through three arteries that branch into a network of smaller vessels.
Coronary Artery Disease affects the blood vessels (arteries) on the surface of the heart.  These arteries bring blood (rich with oxygen and nutrients) to the heart.
These arteries bring blood (rich with oxygen and nutrients) to the heart.
Ageing and other complex factors cause these ordinarily soft and compliant blood vessels to harden. In addition, fat, cholesterol and minerals from the blood are deposited on the inner surface of the coronary arteries. When this material builds up, it forms a plaque that may restrict the blood flow through the coronary artery. Such plaque may also change the surface of the artery from smooth to rough, and these rough surfaces may stimulate the formation of a blood clot, which may slowly build up and narrow the artery even more. A blood clot can also build up quickly and abruptly close off the artery.
WHAT ARE THE AFFECTS OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE?
Narrowed coronary arteries mean the amount of blood that reaches the heart muscle is reduced. Fatigue, tightness in the chest, or a peculiar crushing type of chest pain called angina pectoris may accompany the decreased blood flow. Such symptoms are caused by exercise and emotional stress, which cause the heart to require more blood. However, these symptoms can be handled with adequate rest.
If a coronary artery suddenly closes, blood flow to a part of the heart may stop completely. In this case, some portion of the heart may be permanently damaged. This is often accompanied by severe chest pain that won’t disappear. This is called myocardial infarction, or more commonly, a heart attack. The heart can heal but the muscle is replaced by a scar tissue that doesn’t contract. If the scar is small, recovery can be complete. If the scar is large it may permanently affect the pumping ability of the heart. It is therefore important that blood supply to the heart be restored before a Heart Attack can occur
HOW IS CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE DIAGNOSED?
A Coronary Angiogram shows where the arteries are narrowed or blocked

If you have an increased risk of Coronary Artery Disease or certain symptoms of the disease, your doctor may recommend a Stress test,
exercise or electrocardiogram (ECG). The Stress test measures changes in the electrical activity of your heart while you perform controlled exercise. This test can show if there has been damage to your heart. If the results of the stress test indicate a need for further testing, your doctor may arrange for you to have a Coronary Angiogram, also called Cardiac Catheterization. The coronary angiogram is the most useful test for diagnosing CAD because it allows the doctor to see exactly where the coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked.
Before conducting the angiogram, you will be administered a local anesthetic or pain medicine. The doctor then inserts an introducer sheath into an artery in your groin or through an incision in your arm. Then the doctor inserts a long tube called guiding catheter, into the artery and advances it into the blocked artery. By injecting a contrast dye that can be seen on an X-ray screen, the doctor can observe the arteries in your heart. You may be asked to take a deep breath and hold it while the doctor is conducting the angiogram. Any narrowing or blockage that exists can then be identified. In some cases, the doctor performs a primary angioplasty, or balloon procedure, immediately following the angiogram in order to open the coronary artery for blood flow.
WHAT CAN BE DONE TO RELIEVE BLOCKAGES IN THE CORONARY ARTERIES?
Plaques that block the coronary arteries usually occur in localised portions of the arteries. The part of the artery beyond the narrowing or closure is often not blocked. When the disease is localised in one or two arteries, the blockage can sometimes be opened by stretching or dilating. This is done by using a small balloon on a tube inside the artery. This procedure is called Angioplasty or PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty). Angioplasty has become a relatively common procedure in recent years. Patients around the world will testify to its success in their lives. That said, it still has few risks attached.
Your doctor will discuss the risks that specifically relate to your condition.
HOW IS ANGIOPLASTY PERFORMED?
Patients who have undergone an Angiogram will find Angioplasty procedure almost similar. Angioplasty is also performed in a Cardiac Cath lab. Patients usually receive medication before and during angioplasty procedure to help them relax. You are awake and alert throughout the procedure and are required to respond to the doctors requests during the procedure.
Angioplasty begins by inserting a sheath for the catheter into a blood vessel, most often in the upper leg or groin area, but sometimes in the arm.
A very small balloon catheter is passed through the sheath and into the blood vessel leading to the coronary arteries.


Once the balloon is at the narrowing of the artery, the balloon is centered, it is then inflated to open the blockage.
While every situation is unique, inflation in most cases will last from 30 seconds to several minutes, depending on the nature of the blockage. The balloon is inflated at least two times. However, it may also be inflated to ten or more times.
While the balloon is inflated, some people experience chest pain that is similar to the angina they have experienced. This happens because the balloon temporarily blocks off the flow of blood and the oxygen that it carries to the heart. Patients should report any pain they feel during the procedure to the Doctor. After the block is opened, the balloon is deflated and retracted back through the blood vessel.
CAN ANGIOPLASTY BE PERFORMED IN OTHER ARTERIES?
Balloon Angioplasty has expanded the scope of treatment from patients of Coronary 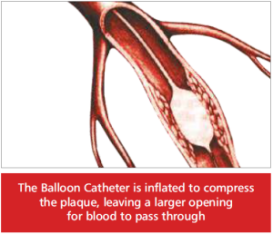 Artery Disease to those suffering from blockages in the other arteries of the body. The procedure is being increasingly used to open blockages in the Carotid artery, Renal artery and other Peripheral arteries.
Artery Disease to those suffering from blockages in the other arteries of the body. The procedure is being increasingly used to open blockages in the Carotid artery, Renal artery and other Peripheral arteries.
WHAT IS A STENT?
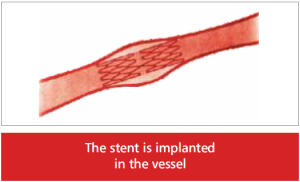
A stent is an expandable mesh tube of a special metal which is designed into a cylindrical wave pattern. The shape and material of the stent offer flexibility for a balloon to adapt to the shape and curves of the artery.


A Stent is implanted to support the artery and keep the vessel open like a structural frame work. It is introduced into your artery just after balloon Angioplasty and is positioned at the site of the obstruction. Implantation of a stent benefits those patients who have a potential for future problems such as block recurrence or restenosis. The stent is implanted permanently in the artery.
WHAT IS PERCUTANEOUS TRANSLUMINAL ROTATIONAL ABLATION (PTCRA)?
One of the treatment options of Coronary Artery Stenosis is the PTCRA or Rotablator System that is used as a stand alone treatment or in conjunction with PTCA.
The Rotablator system is a catheter-based Angioplasty device utilizing a diamond-coated elliptical burr at the tip of a flexible drive shaft. Tracking coaxially over a guide wire and rotating at upto 190,000 revolutions per minute, the burr preferentially cuts away plaque while avoiding healthy tissue. The burr ablates plaque into fine particles that are disposed off by the body’s reticuloendothelial system.
WHAT HAPPENS AFTER THE ANGIOPLASTY PROCEDURE?
After the Angioplasty procedure, patients are taken to an Intensive care unit with special monitoring equipment. Blood pressure, pulse monitoring and ECGs are performed routinely after Angioplasty procedures and do not signify any special problems. If a patient experiences any chest discomfort or pressure, the nurse should be notified immediately.
Recovery in the hospital is most likely a matter of allowing the insertion site to heal before getting up and walking around. Most patients are required to hold their leg or arm straight and still for the first six to eight hours. You may be required to stay in the Hospital for 3-5 days before being discharged to the care of your family doctor. You can resume full activity within a few days of returning home.
Angioplasty is not a cure, but a treatment to reduce the affects of Coronary Artery Disease. It is extremely important to follow your medication regimen without any deviation. Another element for quick recovery involves accommodating lifestyle changes to improve their health and minimise the impact of their heart disease. Several factors are known to contribute to the build up of plaque in the coronary arteries. It is the combination of several of these risk factors, rather than a single factor, that impacts coronary artery disease.
Some of these risk factors such as male sex, age and heredity can only be attended but cannot be changed. However, other factors that can be controlled include:
- High Blood Pressure
- Smoking
- High Blood Cholesterol
- Body Weight
- Diabetes
- Lack of Proper Exercise
- Stress
DIETARY GUIDELINES
FOR PATIENTS WITH CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
Coronary artery disease (CAD) involves the arteries that supply blood to the heart and leads to development of blocks in these vessels which are very small in size (the largest ones being 3 mm in sizes). Despite their small size, these arteries are the primary source of blood supply to the heart, and if they get blocked completely, patients may develop fatal heart attacks.
CAD commonly affects people with some risk factors like
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
- Diabetes Mellitus
- High Blood Cholesterol
- Smoking
- Eating Fatty foods
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Stress
- Family History
If you or your family members have been diagnosed to have CAD, there are some lifestyle changes that need to be adopted immediately and need to be carried on for a life time. Even if you have not had CAD, but are at risk of these factors then certain changes in your life style will help you live long and remain fit with a healthy heart.
PLANNING FOR THE FUTURE
DON’TS
Smoking – The benefits of quitting smoking will start the moment you stop smoking. Smoking affects body in many ways – it damages your lungs, makes your blood vessels stiff and develops blocks in them (which results in paralytic stroke, limbs needing to be amputated, or heart attacks). Each cigarette takes away a certain length of your life and quitting the habit lessens earlier damage and prevents further damage.
Salt– Foods containing excess salt should be avoided, such as
- Pickles or pickled foods
- Chips, or French fries, Poppadoms
- Salted fish
- Caffeine containing beverages (such as Coke, Pepsi, Thums up)
- Sauces
Adding table salt to food should be avoided (i.e. not to add additional salt while eating)
Salt or sodium in the food increases body fluid and increases blood pressure and hence the consumption of salt should be reduced to the bare minimum necessary.
Alcohol and drugs – Consuming alcohol affects the liver primarily but can sometimes cause the heart function to deteriorate, and if that happens there are no medicines or operations that can reverse this condition. Certain drugs like cocaine affects the heart rhythm and can kill people even if consumed in small quantities. All kinds of abusive drugs and alcohol should be avoided.
Fatty foods – The mechanism of development of blocks is by deposition of fat in the walls of the coronary arteries, it is like grit getting accumulated in the pipelines causing the pipe to be partially blocked, over a period of time the block gets worse and becomes complete. The grit in human body is excess fat in the form of cholesterol, this excess fat is formed when we consume far more calories than that are needed on a daily basis. The body converts these excess calories into cholesterol which gets deposited on the walls of arteries. The best way to prevent this phenomenon from occurring is to reduce the calories intake and exercise regularly so that the excess calories are burnt.
FOODS TO BE AVOIDED
- Chips and French fries
- Animal fat
- Whole chicken
- Egg yellow
- Deep fried curries
- Any food that has been cooked in boiled oil
- Deep grilled food
- Sweets particularly made with ghee
- Butter
- Whole milk
- Excess ghee in food or curries
- Coconut oil(This list is not exhaustive but includes most of the food items)
AVOID 5 WHITES
1. Salt
2. Butter
3. Whole milk
4. Sugar
5. Coconut
- Avoid boiled oil or deeply fried foods (samosas, curry puffs, French fries and any food with lots of oil or ghee) ( the more the oil boils, the more poisonous it becomes because it releases toxic fatty acids)
- Avoid excess masala (spices)
DO’S
Eat healthy food: Healthy food constitutes low calorie, high fiber, with vitamins, minerals and other essential elements.
- Low oil content
- Fresh vegetables, salads
- Leafy vegetables
- Fresh fruits
- White fish
- Skinned chicken
- Egg white
- Food rich in fiber content should be consumed like tomatoes, carrots, cabbage, peas, mushrooms, oranges etc.
- Nuts and raisins (at least 1 fist full of nuts and raisins/ day)
- Raw oil on salads like olive oil or sunflower oil is better than boiled oil.
REGULAR EXERCISE – ANGIOPLASTY
Regular exercise in the form of brisk walking or jogging or gym exercises will ensure losing excess calories and helps reduce obesity and blood cholesterol. Exercise is adequate when at the end of it, you are sweating and feel warm. Do not exercise beyond what you are accustomed to, increase the duration slowly over a period of time such as a month or so.
RELAXATION – ANGIOPLASTY
In modern day life, stress has become a part of life and is an important contributor to the increased incidence of heart disease. Find time to relax with family and plan to go on vacations at regular intervals. Practice of yoga helps you relax.
REGULAR MEDICATION – ANGIOPLASTY
Continue your medication as directed by your Cardiologist. Some medications are better taken at the following times.
- Aspirin / Clopidogrel – after breakfast
- Antacid tablets – in the morning after breakfast and sometime in the night after dinner
- Anti hypertensive medication – after food as directed by the Cardiologist
- Anti cholesterol medication – in the night after dinner around 8pm to 10 pm
- Acitrom – in the evening at 6 pm (for patients who underwent valve replacement with metallic valve only)
- Diuretics (water tablets) – in the morning before 8 am and in the afternoon between 12noon and 2 pm
MEDICATION – ANGIOPLASTY
Never stop any medication prescribed post-stenting, heart operations or after having been diagnosed for a heart problem. Consult your Cardiologist before you discontinue, as such medication is normally for a life time. Also, these medicines are part of secondary prevention strategy, aimed at preventing the disease from getting worse and in some instances to improve some of the blocks.
Many of these medicines help your heart recover from the previous occurences such as heart attacks. Medicines aimed at reducing blood pressure, control of diabetes and reduction of cholesterol have a protective affect and help the stent or bypass graft to function for a long time or else blocks can develop in these areas again.
Aspirin has been found to have many protective effects such as prevention of clot formation, reduces block size, and increases longevity of the stent or graft. Clopidogrel is another important medicine that acts similar to Aspirin and is very helpful in keeping stents working and is essential for at least the first 6 months to 1 year after special stent insertion (Drug Eluting Stents).
Therefore do not stop these medications until your Cardiologist asks you to do so.
GENERAL ADVICE
- Try and rotate the use of oils between rice bran oil, sunflower oil or olive oil.
- Try and use 3 – 4 teaspoons of oil a day (roughly ½ a litre of oil/ person/ month).
- Restrict use of salt / do not add table salt to food.
TYPICAL FOOD INTAKE FOR A CARDIAC PATIENT
(SAMPLE MENU)
BREAK FAST
- 2 Idlis with dhal powder or sambhar
- 2 Pulkas with veg curry
- 2 Bread slices white omlette
- Vegetable sandwiches
- Cornflakes
- Oat porridge / upma
- Tea / coffee / semi skimmed or soya milk
- 1 glass of lime juice in cold / warm water
LUNCH
- ½ cup vegetable salad each (cucumber, tomato, onion, green salad leafs)
- Cereal
- 1 cup boiled vegetables
- 1 cup vegetable curry with very little oil
- 1 cup thin dhal / peas / sambhar
- 1 cup rasam
- 1 cup skimmed milk curd
- Meat with as little fat as possible – occasionally
TEA TIME
- Coffee / tea / diluted milk
- Sprouted pulses / Marie biscuits / puffed rice
DINNER
- 2 – 3 pulkas / 1 cup of rice
- Boiled vegetables / vegetable curry
- 1 cup rasam
- 1 glass of butter milk
http://counter3.01counter.com/private/counter.js?c=6dd68d40b128c66591c25fa4d57790f4
